What is a Floor Joist? Types, Materials, and Installation
Have you ever wondered what keeps the floors in your home so sturdy and reliable? Whether you’re walking across your living room, kitchen, or bedroom, there’s a hidden hero beneath your feet making sure everything stays in place.
That hero is the floor joist.
But what is a floor joist?
A floor joist is a horizontal structural member that supports the floor, distributing weight evenly across the structure and preventing sagging or bending.
In this article, we’ll dive into “What is a Floor Joist?” and explore everything you need to know about this crucial component in construction.
We’ll cover the importance of floor joists, the different types available, the materials used, standard sizes, and spacing, and even guide you on how to install them.
What is a Floor Joist?
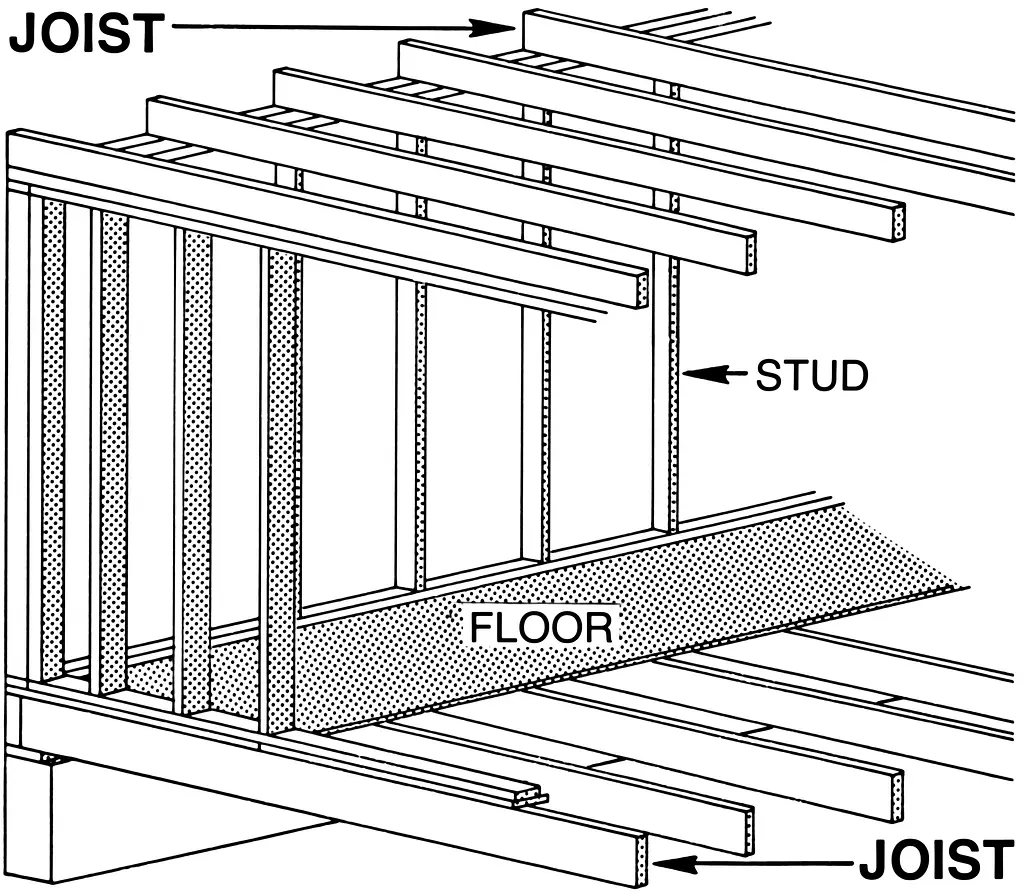
So, what exactly is a floor joist?
It same like the skeleton of a house – the floor joists are like the bones that give strength and structure to your floors.
A floor joist is a horizontal structural member that spans an open space, usually between walls or beams, to provide support for a floor.
These joists are essential in distributing weight evenly across the structure, ensuring that your floors can bear the load of furniture, appliances, and people without sagging or collapsing.
Importance of Floor Joists in Construction
Floor joists play a vital role in construction, and their importance cannot be overstated. Here’s why:
- Structural Integrity: Floor joists provide the necessary support to hold up the weight of the floor and everything on it. Without them, floors would be weak and prone to damage or collapse.
- Weight Distribution: They help distribute the weight of the floor evenly across the structure, preventing any single point from bearing too much load. This ensures a stable and safe environment.
- Prevent Sagging: Properly installed floor joists prevent floors from sagging or bending, which can lead to uneven surfaces and potential hazards.
- Support for Subflooring: They offer a sturdy base for subflooring materials, which are then covered by the finished flooring. This combination provides a solid, level surface for everyday activities.
In essence, floor joists are the unsung heroes that keep our homes safe and sound.
Types of Floor Joists
When it comes to floor joists, there are several types to choose from, each with its own set of advantages and best-use scenarios. Here are the most common types:
1. Solid Lumber Joists
Solid lumber joists are the traditional choice and have been used in construction for centuries. They are made from individual pieces of lumber, usually 2×8, 2×10, or 2×12. These joists are straightforward to work with and widely available, making them a popular choice for many builders.
2. Engineered Wood Joists
Engineered wood joists, also known as I-joists, are made from a combination of wood products and adhesives. They are designed to be stronger and more uniform than solid lumber joists. I-joists have a characteristic “I” shape, which gives them their name and allows them to span longer distances without support.
3. Metal Joists
Metal joists, typically made from steel, are used in commercial and industrial construction. They offer exceptional strength and can support heavy loads over long spans. However, they are more expensive and require specialized tools and expertise for installation.
4. Open Web Trusses
Open web trusses are a type of floor joist made from a combination of wood and metal. They feature an open web design, which allows for easy installation of plumbing, electrical, and HVAC systems. These trusses are strong and versatile, making them a popular choice for modern construction projects.
Materials Used for Floor Joists
The materials used for floor joists vary based on the type of joist and the specific needs of the construction project. Here are the most common materials:
- Wood: Traditional and engineered wood products are the most common materials used for floor joists. Wood is readily available, relatively affordable, and easy to work with.
- Steel: Steel is used for metal joists and offers superior strength and durability. It is ideal for commercial and industrial applications.
- Composite Materials: Some floor joists are made from composite materials that combine wood fibers and plastic. These joists offer increased resistance to moisture and pests.
Standard Sizes and Spacing for Floor Joists
The size and spacing of floor joists are crucial factors in ensuring the structural integrity of a building. Here are the standard sizes and spacing guidelines:
Standard Sizes
The size of a floor joist is typically expressed in terms of its nominal dimensions (width x depth). Here are the standard sizes:
- 2×8 (1.5″ x 7.25″)
- 2×10 (1.5″ x 9.25″)
- 2×12 (1.5″ x 11.25″)
Standard Spacing
The spacing of floor joists refers to the distance between the centers of adjacent joists. Common spacing options include:
- 12 inches on center (OC)
- 16 inches on center (OC)
- 24 inches on center (OC)
Example Table
| Joist Size | Maximum Span (in feet) at 16″ OC | Maximum Span (in feet) at 24″ OC |
| 2×8 | 12.5 | 10.5 |
| 2×10 | 16.5 | 13.5 |
| 2×12 | 19.5 | 15.5 |
These sizes and spacing guidelines are general recommendations. It’s always important to consult local building codes and a structural engineer for specific projects.
How to Install Floor Joists: A Step-by-Step Guide

Installing floor joists might seem like a daunting task, but with the right tools and a bit of patience, it’s a manageable project. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
Step 1: Gather Your Tools and Materials
You’ll need joists, a measuring tape, a level, a saw, a hammer, nails, or joist hangers, and safety equipment.
Step 2: Measure and Mark
Measure the area where the joists will be installed. Mark the positions on the ledger boards or beams where each joist will go, following the standard spacing guidelines.
Step 3: Cut the Joists
Cut the joists to the appropriate length, ensuring they fit snugly between the walls or beams.
Step 4: Install Joist Hangers
If using joist hangers, attach them to the ledger boards or beams at the marked positions. Ensure they are level and securely fastened.
Step 5: Position the Joists
Place the joists into the hangers or onto the ledger boards, ensuring they are level and properly spaced.
Step 6: Secure the Joists
Secure the joists using nails or screws. Double-check that everything is level and properly aligned.
Step 7: Install Bridging or Blocking
Install bridging or blocking between the joists to provide additional stability and prevent twisting.
Step 8: Inspect Your Work
Finally, inspect your work to ensure everything is secure, level, and properly spaced.
Common Problems with Floor Joists and How to Fix Them
Floor joists, like any structural component, can encounter issues over time. Here are some common problems and how to fix them:
- Sagging Joists: Reinforce with sister joists or add support beams.
- Cracked or Damaged Joists: Replace the damaged section or reinforce with additional lumber.
- Rotten Joists: Replace the affected joists and address any moisture issues to prevent future problems.
- Bouncy Floors: Add bridging or blocking, or increase the size or number of joists for better support.
- Noisy Floors: Use construction adhesive and screws to secure subflooring and reduce movement.
Conclusion
It is imperative for anyone involved in construction or home improvement to understand “What is a Floor Joist?” These critical components ensure the stability and safety of your floors, providing a solid foundation for daily life.
Whether you’re building a new home, renovating an existing space, or simply curious about how your house works, knowing about floor joists gives you valuable insight into the structural integrity of your living environment.
By following the guidelines for types, materials, sizes, and installation, you can ensure your floors remain strong and reliable for years to come.
FAQs
Related Articles:
- How to Stagger Vinyl Plank Flooring: A Complete DIY Guide
- What is LVP Flooring? Benefits, Types, and Installation Tips
- Which Direction to Lay Vinyl Plank Flooring? Expert Tips

